
Are you experiencing a decrease in platelet count after taking Pantoprazole? It could be a sign of thrombocytopenia, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. Thrombocytopenia is a disorder characterized by low levels of platelets in the blood, which can lead to abnormal bleeding and bruising.
Don’t ignore the warning signs – if you suspect that Pantoprazole is causing thrombocytopenia, consult your healthcare provider right away to discuss alternative treatment options.
Your health is important – be proactive and take action if you notice any unusual symptoms while taking Pantoprazole. Your well-being is worth it!
Possible Mechanism and Risks
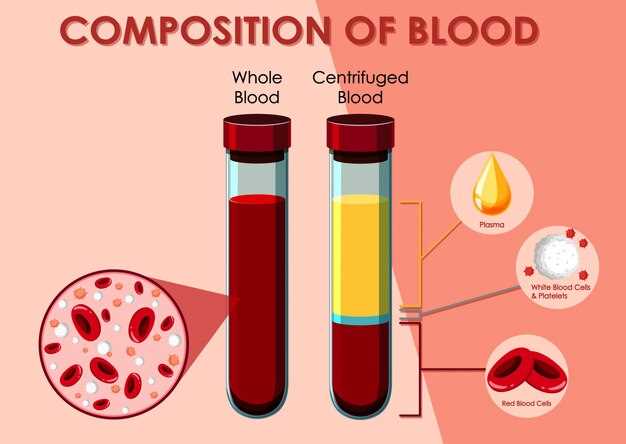
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by a low platelet count in the blood, which can lead to excessive bleeding and easy bruising. Pantoprazole, a proton pump inhibitor commonly used to treat acid-related disorders, has been associated with the development of thrombocytopenia in some patients.
The exact mechanism by which pantoprazole causes thrombocytopenia is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve an immune-mediated response in which the drug stimulates the production of antibodies that target and destroy platelets. This results in a decrease in the number of functional platelets in the bloodstream.
Patients taking pantoprazole may be at an increased risk of developing thrombocytopenia if they have a history of autoimmune disorders or if they are concurrently taking other medications that can affect platelet function. It is important for healthcare providers to monitor platelet counts in patients taking pantoprazole and to promptly investigate any signs or symptoms of thrombocytopenia, such as unexplained bruising, bleeding gums, or nosebleeds.
Possible Mechanism and Risks
Thrombocytopenia induced by pantoprazole is believed to be an immune-mediated response, where the drug triggers the body’s immune system to attack and destroy platelets. This can lead to a decrease in the number of platelets in the bloodstream, resulting in a higher risk of bleeding and bruising.
Some of the potential risks associated with pantoprazole-induced thrombocytopenia include:
- Increased susceptibility to bleeding
- Easy bruising
- Prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or injuries
It is essential to monitor platelet levels regularly in patients taking pantoprazole to detect thrombocytopenia early and provide appropriate management.
Detection and Diagnosis
Diagnosing thrombocytopenia caused by Pantoprazole often involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Blood tests, such as a complete blood count (CBC) with platelet count, can help in detecting low platelet levels. Additionally, a bone marrow aspiration or biopsy may be recommended to evaluate the production and functioning of platelets.
Other diagnostic tests may include tests for specific antibodies that target platelets, imaging studies to assess the spleen and liver (organs involved in platelet destruction), and ruling out other potential causes of thrombocytopenia.
Early detection of Pantoprazole-induced thrombocytopenia is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment and preventing complications. If you experience unexplained bruising, bleeding, or other symptoms of low platelet levels while taking Pantoprazole, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation.
Treatment and Management
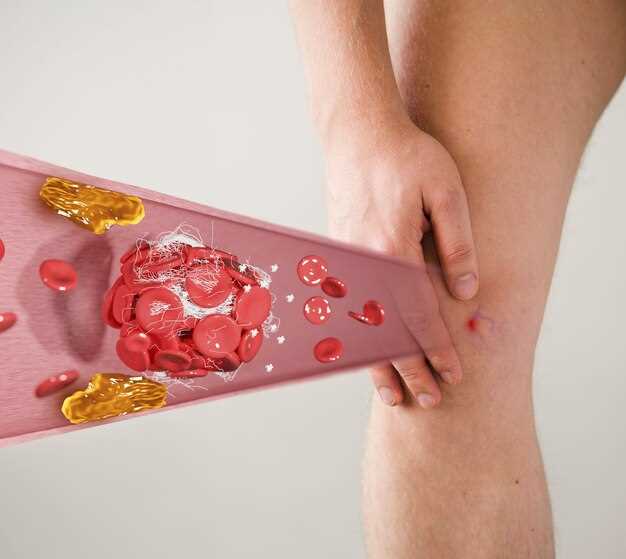
Treatment options for thrombocytopenia caused by pantoprazole depend on the severity of the condition and the underlying cause. In mild cases, discontinuation of pantoprazole may be sufficient to restore platelet levels to normal. However, in more severe cases or if the thrombocytopenia is persistent, other treatment options may be considered.
One approach is to switch to an alternative medication that does not have a similar effect on platelet levels. This may involve using a different class of acid-suppressing drugs or exploring non-pharmacological treatments for gastrointestinal issues.
In some cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary to quickly increase platelet levels and prevent bleeding complications. However, this approach is usually reserved for severe cases or emergencies.
It is important for patients with thrombocytopenia to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their platelet levels and adjust treatment as needed. Regular blood tests may be necessary to track changes in platelet counts and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and avoiding factors that can further lower platelet levels, such as certain medications or excessive alcohol consumption, can help manage thrombocytopenia and reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing thrombocytopenia caused by Pantoprazole involves certain lifestyle modifications and precautions. Here are some key measures to consider:
- Avoid regular or prolonged use of Pantoprazole without consulting your healthcare provider.
- Follow your doctor’s prescribed dosage and regimen strictly.
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for platelet production.
- Avoid excessive alcohol consumption as it may exacerbate the condition.
- Engage in regular physical activity to promote overall health and blood circulation.
- Monitor any signs of bruising, bleeding, or unusual tiredness and report them to your doctor promptly.
By adhering to these lifestyle changes and being vigilant about your health, you can reduce the risk of developing thrombocytopenia associated with Pantoprazole.
